What is Ayurveda?
Ayurveda is to be the oldest healing science Sanskrit ayur, meaning "life" and veda, meaning "knowledge" or "science." Ayurvedic knowledge originated in India more than 5,000 years ago and is often called the “Mother of All Healing.” It stems from the ancient Vedic culture and was taught for many thousands of years in an oral tradition from accomplished masters to their disciples. Some of this knowledge was set to print a few thousand years ago, but much of it is inaccessible. The principles of many of the natural healing systems now familiar in the West have their roots in Ayurveda, including Homeopathy and Polarity Therapy. The concept of ayurveda is based on two major principles. The first principle is that the body and mind are interconnected, and the second principle is that the mind is powerful enough to heal the body. The body is cured of illnesses only when one's awareness of the self-expands.
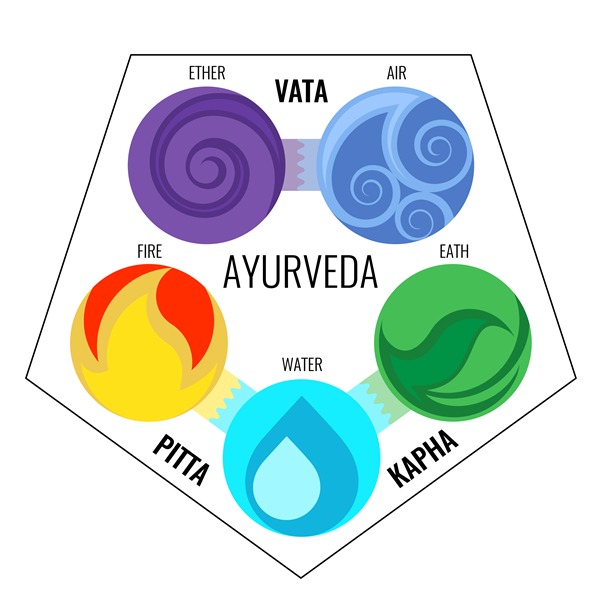
If your mind, body, and spirit are in harmony with the universe, you have good health. When something disrupts this balance, you get sick. Among the things that can upset this balance are genetic or birth defects, injuries, climate and seasonal change, age, and your emotions. Those who practice Ayurveda believe every person is made of five basic elements found in the universe: space, air, fire, water, and earth. These combine in the human body to form three life forces or energies, called doshas. They control how your body works. They are Vata dosha (space and air); Pitta dosha (fire and water); and Kapha dosha (water and earth). Everyone inherits a unique mix of the three doshas. But one is usually stronger than the others. Each one controls a different body function. It’s believed that your chances of getting sick -- and the health issues you develop -- are linked to the balance of your doshas.